The research is conducted within 6 study areas covering urban and rural, common and protected areas with tourist, industrial or agricultural use. They include municipalities classified as urban, rural and urban-rural. The selected areas are diverse in terms of topographic conditions, land cover and the location of nature conservation areas and industrial zones within their borders, and represent many of the landscape types found in Poland.
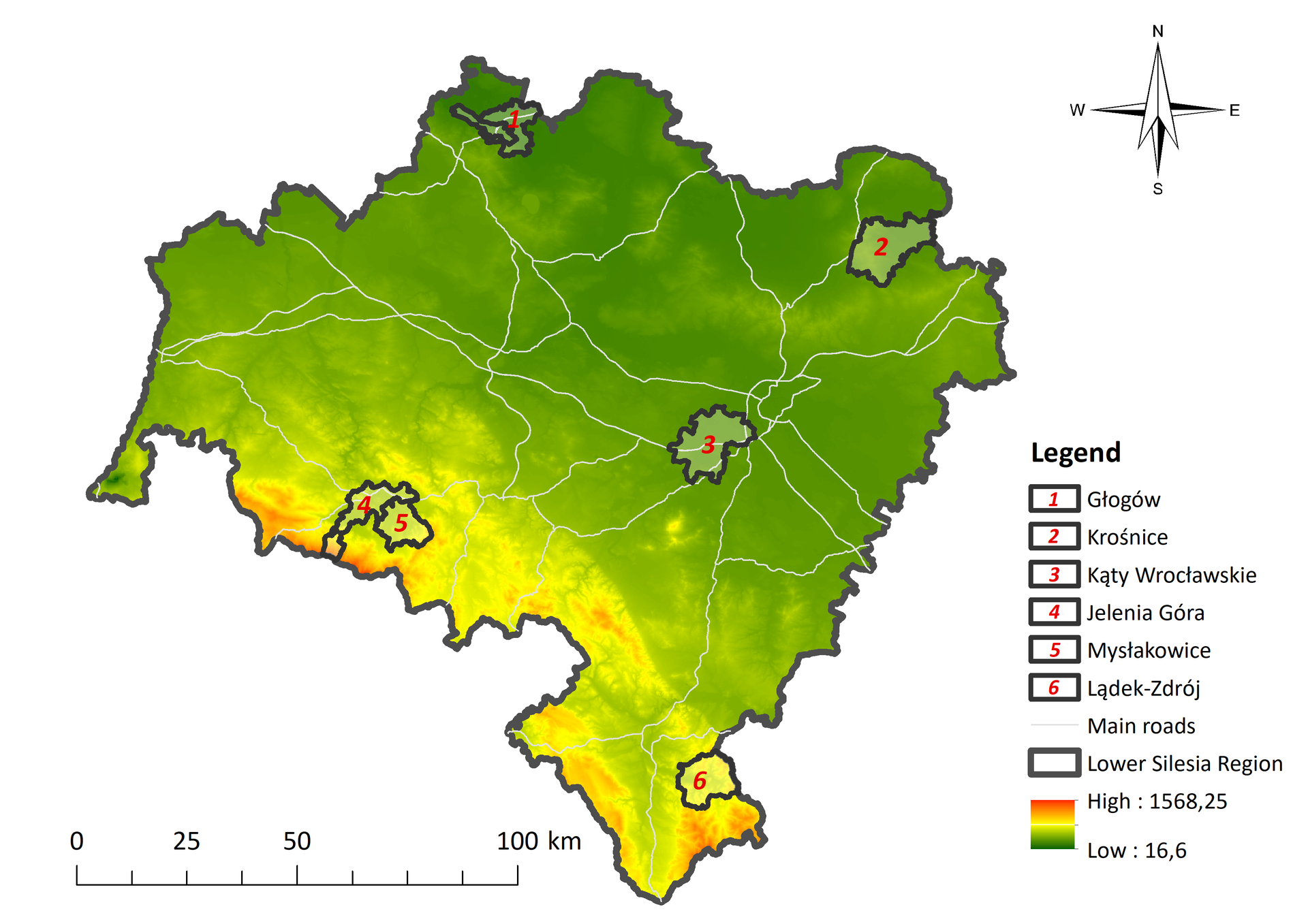
During preliminary study, all the municipalities in the Lower Silesian province were grouped into six groups: cities with county rights, municipalities located in the suburban zone of Wroclaw, municipalities located in mountainous areas, municipalities located in flat areas, industrial municipalities, and municipalities located entirely within protected areas. From each group in the Lower Silesian province, one municipality with the highest landscape diversity was selected as the study area:
the city of Jelenia Góra - a medium-sized city with county rights located in the southwestern part of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, at the foot of the Karkonosze Mountains, next to the Karkonosze National Park, on the Bóbr River, an area representing mainly a metropolitan landscape with historical and modern parts, suburban, mountainous and forest landscape as well as mosaic landscape;
municipality of Kąty Wrocławskie – an urban-rural municipality with a flat character, located in the central part of the Lower Silesian province within the suburban zone of Wrocław; it lies on the Silesian Lowlands in the eastern part of the Wrocław Plain, near the International Airport in Wrocław, A4 freeway runs in the central part of the municipality, it represents an urban, suburban, rural, communication and forest landscapes;
municipality of Lądek-Zdrój - an urban-rural municipality, a well-known tourist area with a large number of forests, recreational areas and hotels, popular with tourists due to its status as a health resort, located in the southern part of the Lower Silesian province, in the Eastern Sudetes, represents a forest, urban and rural landscapes;
Krośnice commune – a rural commune comprising mainly flat agricultural and forest areas with a large number of breeding ponds and a few hills, located in the northeastern part of the Lower Silesian province, almost entirely within the boundaries of the Barycz Valley Landscape Park and two Natura 2000 areas, represents mainly a rural, forest and wetland landscapes.
Mysłakowice commune – a rural commune comprising mountainous areas, with a large number of forests, areas used for agriculture and palace and park complexes, located in the southwestern part of the Lower Silesian province, at the foothills of the Rudawy Janowickie Mountains, within the Rudawy Landscape Park, represents forest, rural, mosaic and suburban landscapes.
the city and municipality of Glogow – an urban and rural municipality, encompassing an area located in the Oder River valley, in the northwestern part of the Lower Silesian province, largely used as a site for mining, represents water, urban and mining landscapes.
A total of 117 landscape units representing the following landscapes were identified within the selected study areas: